In this post, you will learn what technical SEO is and what are the best practices to ensure that your website is technical SEO-friendly.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing your website to help search engines access, crawl, understand, and index your pages without any problems. The main goal of technical SEO is to optimize the infrastructure of a website to improve its rankings in the search results.
It is called “technical” because it has nothing to do with the “actual” content of the website or website promotion.
Why Is Technical SEO Important?
Technical SEO is a very important step in SEO. Any technical SEO issues will negatively impact your website’s SEO performance in Google and other search engines.
If search engine crawlers cannot access your pages, your content will not be in their index and will not appear for any searchers.
In addition, some technical SEO factors like mobile-friendliness, website load speed, and HTTPS and crucial Google ranking factors.
What Is The Difference Between SEO and Technical SEO?
Technical SEO involves optimizing the technical part of a website (like code), while SEO is the process of optimizing all aspects of a website for search engines. Technical SEO is part of the SEO process.
To get the whole picture, look at the diagram below, which shows the three main pillars of SEO: Technical SEO, On-Page SEO, and Off-page SEO.
On-page SEO is related to content and how you can make it more relevant to what the user is searching and off-page SEO is the process of getting mentions (links) from other websites to increase trust during the ranking process.
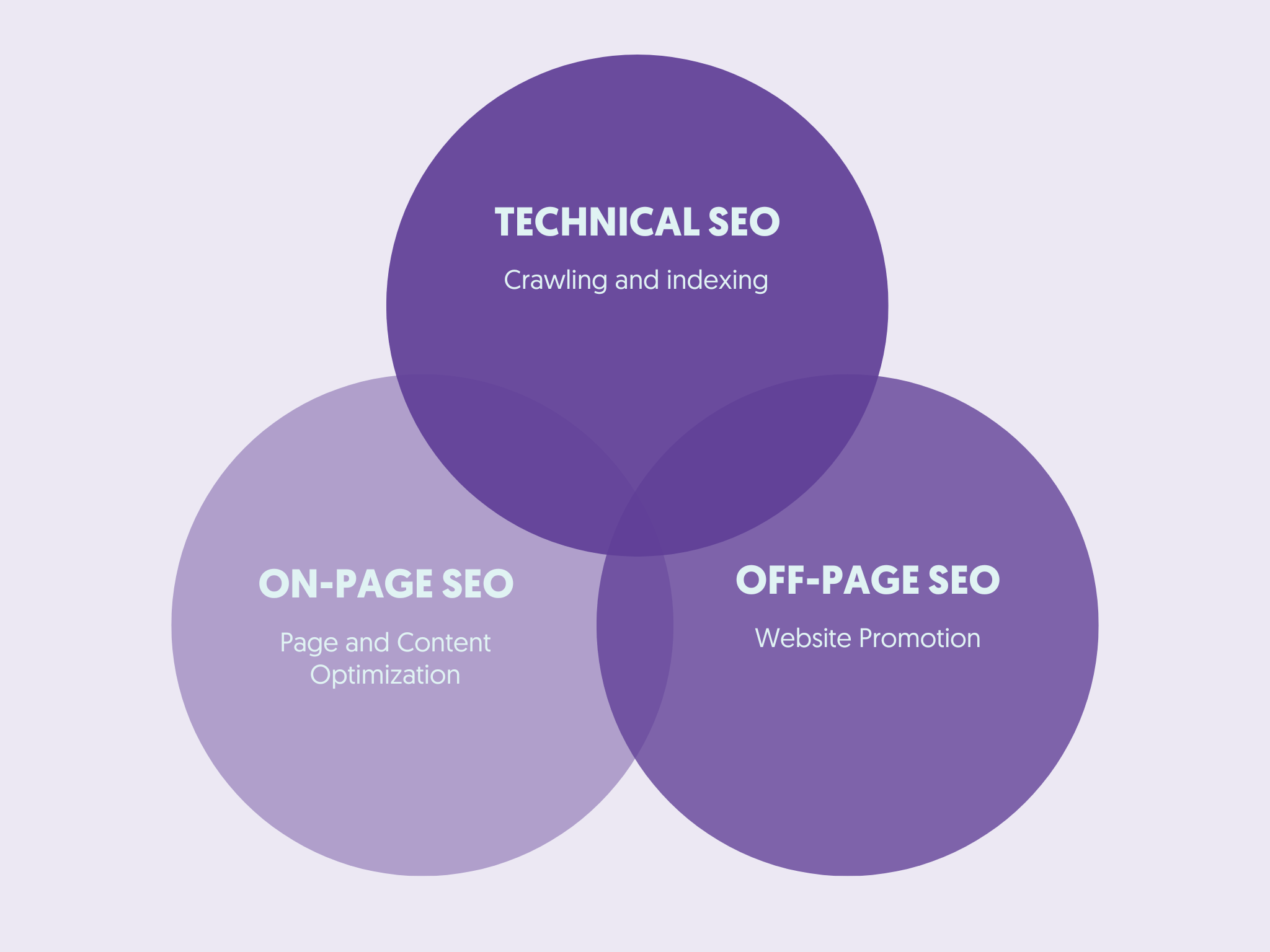
As you can see, there are no clear boundaries between technical, on-page, and off-page SEO because they all have to work together for a fully optimized website.
Understanding Crawling and Indexing
To understand what technical SEO covers, you need to learn how search engines work and in particular about the crawling and indexing phase.
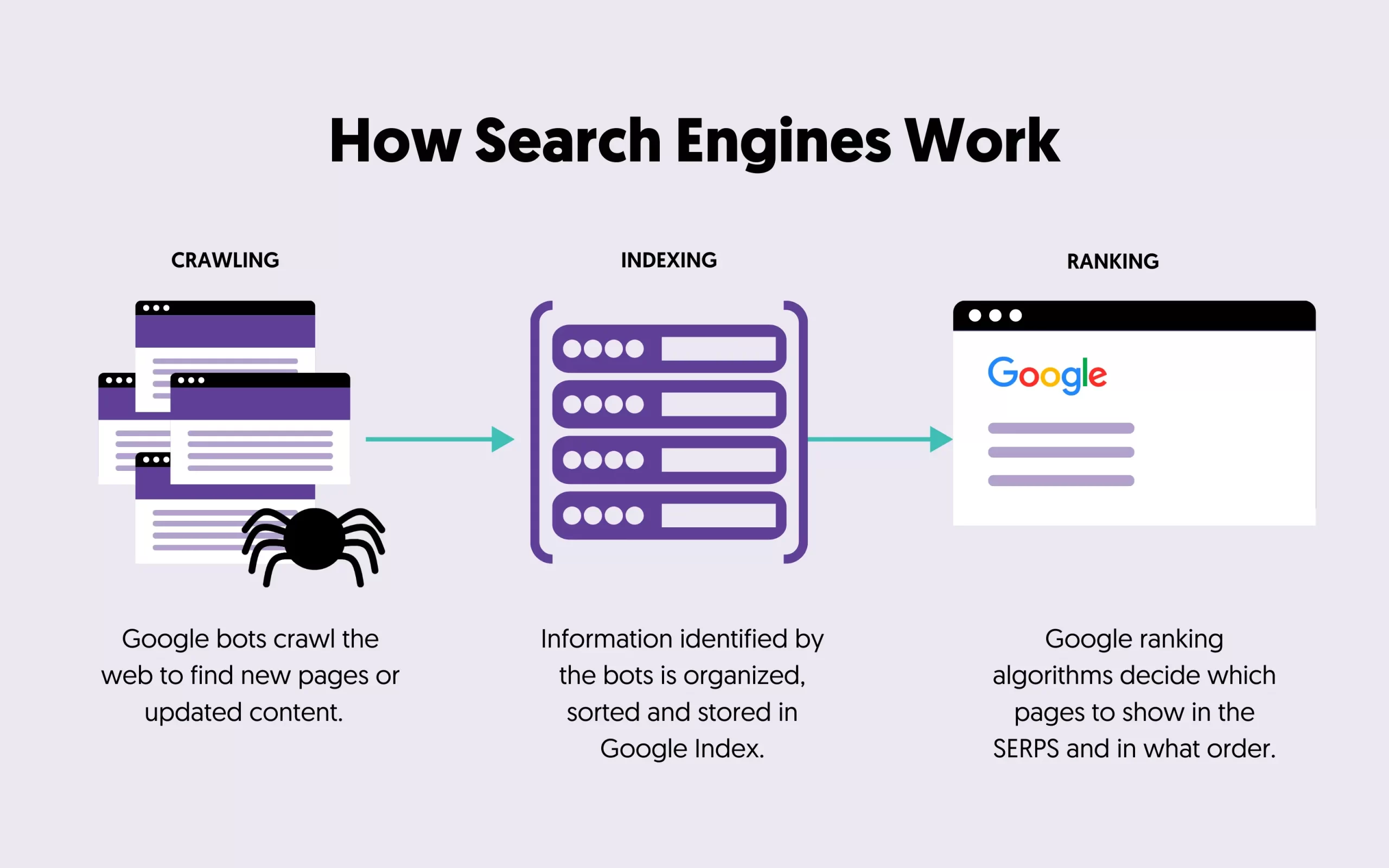
The first step taken by search engines, long before answering a search query, is the crawling process. During this process, search engines are looking for publicly available web pages to add to their index.
During the indexing phase, information identified by the bots is organized, sorted, and stored in their database (index) so that they are later accessed by the ranking algorithms to provide precise answers to the queries entered by users.
Some Technical SEO examples associated with these two phases include optimizing your robots.txt file and the noindex tag.
robots.txt
Robots.txt is a text file residing in the root directory of your website that gives instructions to search engines as to which pages of your website they can crawl and add to their index.
The format of this file is very simple and in the majority of cases, you don’t have to make any changes to it. Here are a couple of examples:

What is important though is to check and ensure that there are no false blockings that will discourage search engine crawlers from indexing your website.
For more information, you can read: How to optimize and validate your robots.txt
The noindex tag.
Another way to control which pages search engines can add to their index is the “noindex tag”. By placing the tag in the head section of a page, you instruct search engines NOT to index the particular page. Here is an example of a noindex tag:

You can use this technique to ensure that crawlers will not index pages that are not important to your website. Typical examples include ‘thank you’ pages, landing pages used for Facebook and Google Ads, and autogenerated tag pages.
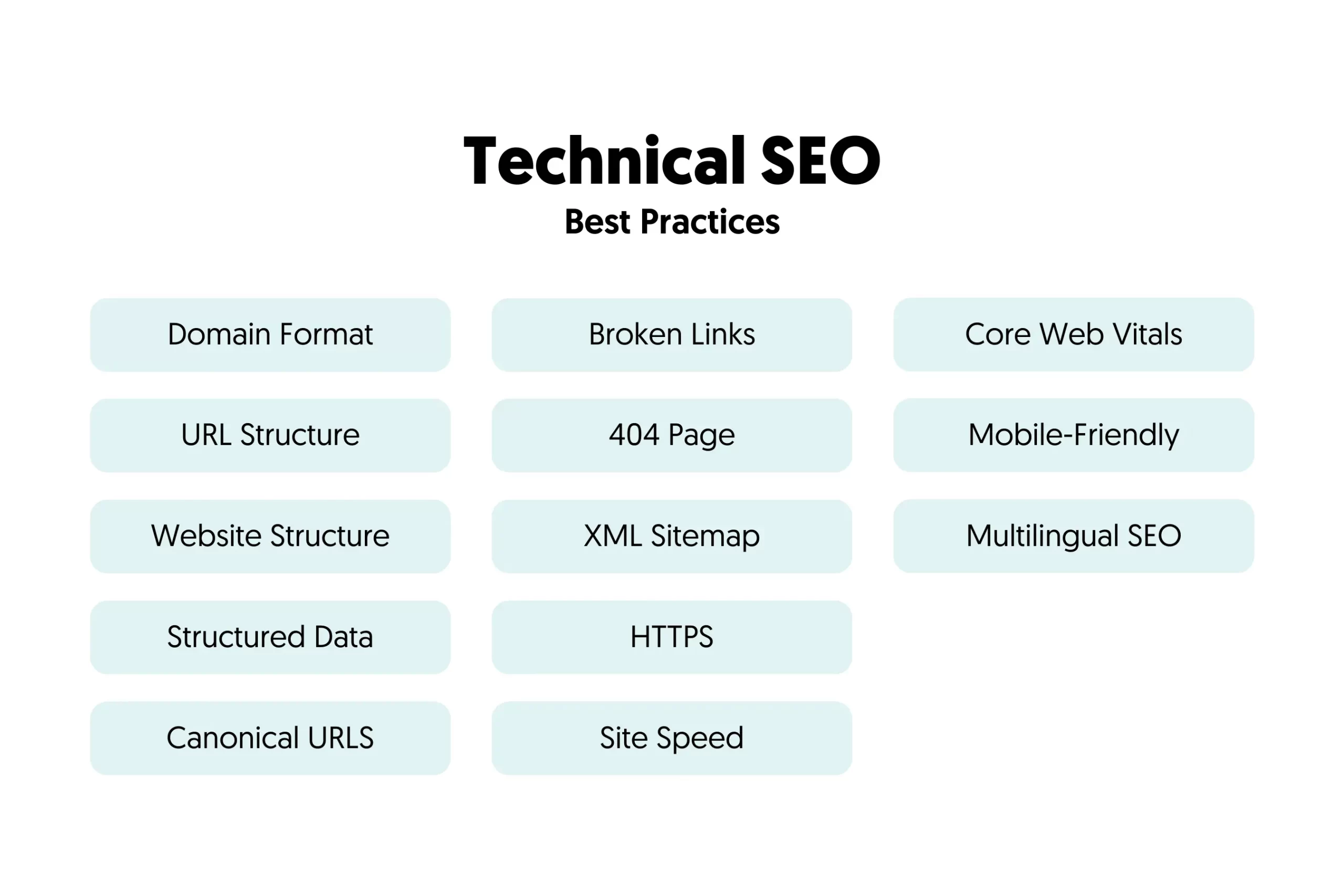
Technical SEO Best Practices
Follow these techniques to fully optimize your website for technical SEO.
- Choose Your Domain Format
- Optimize Your URL Structure
- Navigation and Website Structure
- Structured Data Markup
- Check Your Canonical URLs
- Find And Fix Broken Links
- Optimize Your 404 Page
- XML Sitemap Optimization
- SSL and HTTPS
- Website Speed
- Optimize For Core Web Vitals
- Mobile-Friendly Website
- Multilingual Websites
1. Choose Your Domain Format
One of the first technical SEO settings you need to configure is how you want your domain to be accessible by search engines and users. By default, a website is accessible with www and without www in front of a domain. For example, if your domain is example.com, your website can be accessed by:
- https://www.example.com
- https://example.com
While this is okay for users, it is confusing for search engines because they consider these as two different websites.
This means you may encounter indexing issues, duplicate content problems, and loss of page rank.
To solve this problem, you must decide which format you want to use and use it consistently throughout the lifetime of your website.

There is no SEO advantage to choosing one format over the other. It’s a matter of personal preference. I prefer to have www in front of my domains because it seems more natural to me but there is nothing wrong if you decide to go with the non-www version.
If you’re on WordPress, make sure that both the WordPress Address and Site Address point to your preferred version.

To test that your website is configured correctly, open a browser window and type https://example.com. If your preferred domain is set to https://www.example, then the page should automatically redirect to https://www.example.com.
For a detailed walkthrough, read our guide on www or no www.
2. Optimize Your URL Structure
The next item in your technical SEO list is to revise the URL structure of your website. By URL structure, we mean the format of your URLs.
Best SEO practices dictate the following about URLs:
- Use lowercase characters
- Use – to separate words in the URL
- Make them short the descriptive
- Avoid using unnecessary characters or words
- Use your target keywords in the URL without keyword stuffing
In general, once you define the format of your permanent link structure, the only thing you will have to do is to optimize your URLs when publishing new content.
If you are using WordPress as your CMS, you will notice that when creating a new post, it takes your post title and creates the URL.

For example, if this is your post title “10 Technical SEO Best Practices For Beginners”, the URL generated by WordPress will be:
https://www.example.com/10-technical-seo-best-practices-for-beginners.
This is not bad, but you can make it shorter like this:
https://www.example.com/technical-seo -which is more targeted and easier to remember.
For more information and examples, read the following post: What is an SEO-Friendly URL?
3. Navigation and Website Structure
The website structure is a very important SEO factor for many reasons. Users are more likely to stay on a website longer and find out what they want faster, and search engines can understand and index a website more easily.
Google does take into account the overall site structure when evaluating a particular page, and this is something that shouldn’t be overlooked.
Best practices indicate that you should use a hierarchical site structure (see example below). A website’s crawling starts from the homepage and crawlers follow links from the homepage to discover other pages.

As a rule of thumb, make sure that each page on your website is accessible in less than 3 clicks from the homepage.
If have enough pages around a specific topic area, create optimized category pages to group these related pages.
Another element that helps your technical SEO is breadcrumb lists (aka breadcrumb menus).
A breadcrumb menu is a set of links at the top or bottom of a page that allows users to navigate to a previous page (usually the category page) or the home page of a website.

A breadcrumb menu serves two primary purposes: it helps users navigate a website easily without having to press the back button on their browsers, and it gives another hint to search engines about the structure of a website.
Breadcrumbs are mentioned as an SEO element in various SEO Guides because they are highly recommended by Google.
If you don’t already have breadcrumbs enabled, ensure they are enabled on your website and have the proper schema. Read our breadcrumbs SEO guide to learn more.
4. Structured Data Markup
Structured data has gained more and more importance in the last few years because Google heavily uses it in Search Results.
What is structured data?
In simple terms, structured data is code you can add to your web pages that is visible to search engine crawlers only and helps them understand the context of your content. It’s a way to describe your data to search engines in a language they can understand.
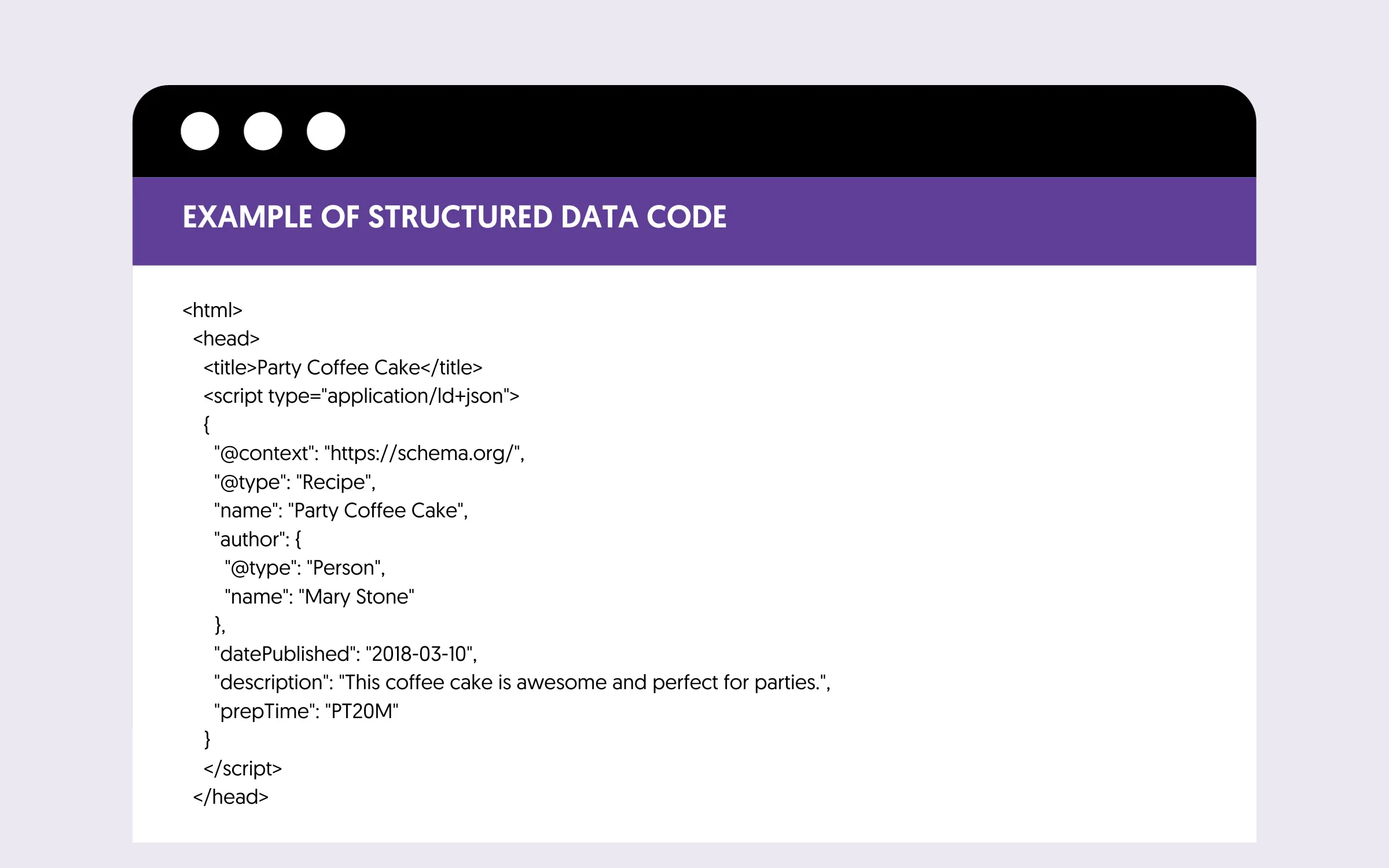
How is structured data related to technical SEO?
Although structured data has to do with the content of a website, it is part of technical SEO because you need to add code to your website to get it right. Usually, you add the structured data definition once and then you don’t have to do anything about it.
For example, in the case of breadcrumbs, you need to configure your structured data once, and no further actions are required. The same goes for articles. Once you add the correct structured data definition to your CMS, it will automatically be applied to new content.
What is the benefit of using structured data?
It can help you enhance the presentation of your listings in the SERPS (like gaining featured snippets) and increase your CTR.

What are the uses of structured data?
There are many ways you can use structured data to describe your content. The most popular are articles, recipes, reviews, products, job postings, local businesses, and more. You can view the complete list here.
5. Check Your Canonical URLs
Every page of your website should have a canonical URL. This is defined by adding the canonical tag in the HEAD of your posts and pages like this:
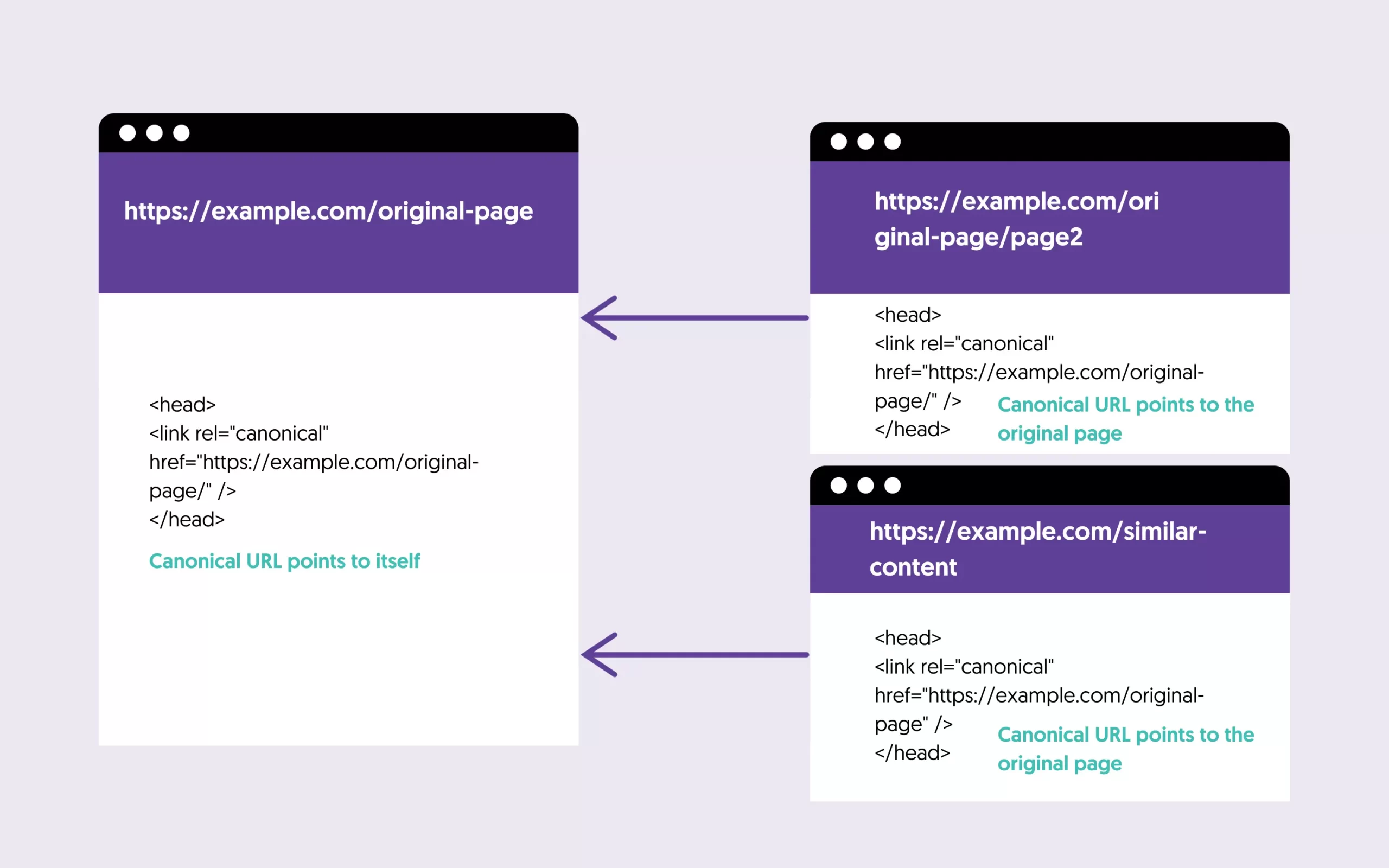
What is a canonical URL?
It’s a simple way to tell Google which version of a page to take into account when indexing your website. The concept is similar to the domain format where a single page is accessible through various URLs.
You can use the rel=”canonical” when you have pages with similar content for paging purposes and to avoid duplicate content issues.
As a general rule, you should specify a canonical URL for all your website pages.
The simplest way to check if your website provides a canonical URL is to visit any of your pages, right-click anywhere on the page, and select VIEW SOURCE. Search for rel=canonical and investigate the value.
If you cannot find any reference to canonical then you can either use a plugin to add this automatically (if you are on WordPress, you can use Yoast SEO) or hire a developer to make the necessary changes to your code.
As with other technical SEO elements, once you set your website to output the canonical URL correctly, you don’t have to do anything else.
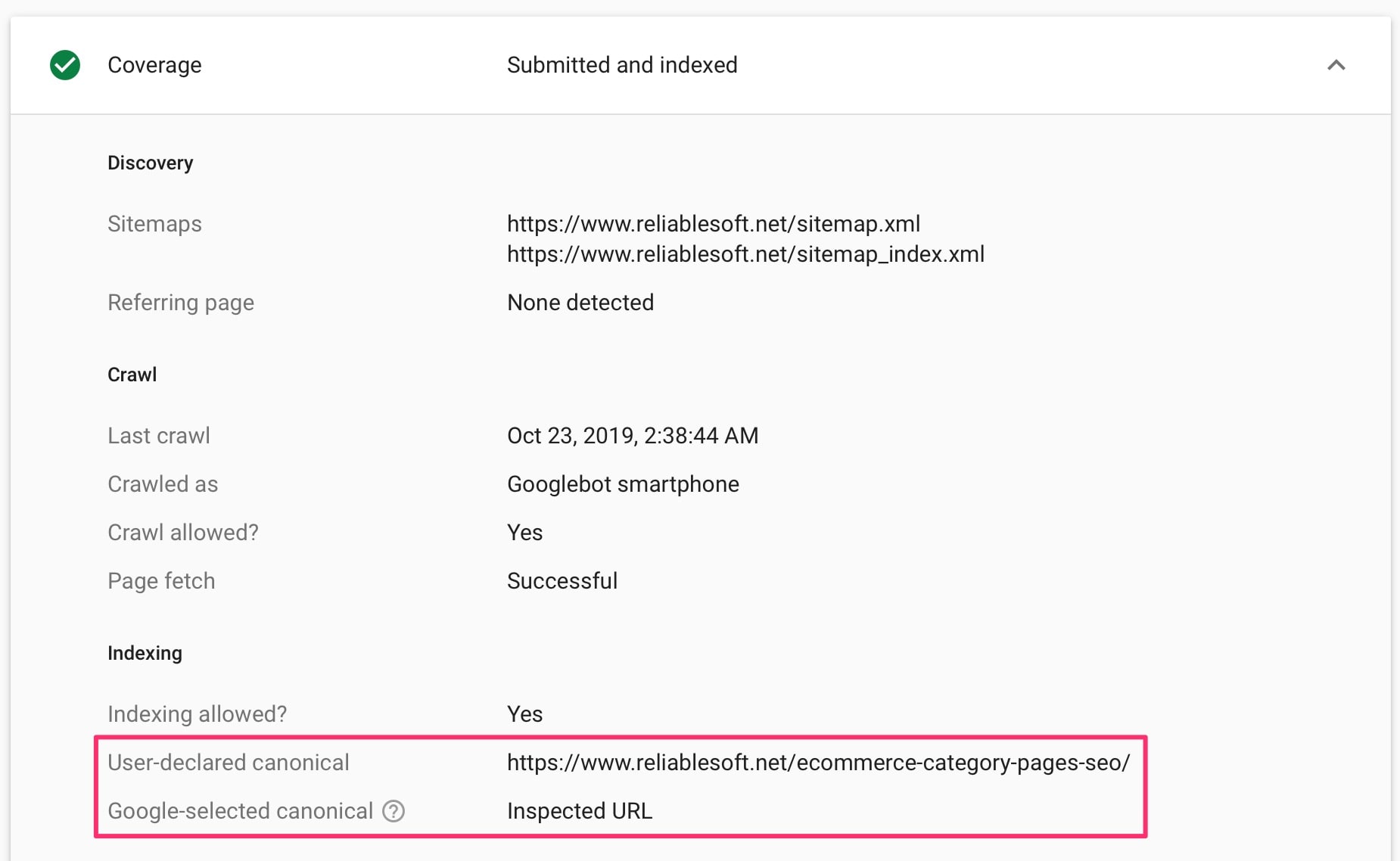
You can use the Inspection Tool (part of Google Search Console) to check your canonical URLs on Google.
6. Find And Fix Broken Links
As part of your technical SEO review, you must find and fix any broken links on your website. It’s bad for the user experience, and any backlinks pointing to missing pages lose their value.
You can find broken links using the Not Found (404) report in Google Search Console or a free tool like W3C Link Checker.

When you find your broken links, you have three options:
- Fix them by changing the links to point to the correct page
- Redirect the missing URLs to a valid page
- Show a 404 (Not Found) page to users
7. Optimize Your 404 Page
A 404 page is shown to the users when the URL they visited does not exist on your website. Maybe the page was deleted, the URL was changed, or they mistyped the URL in their browsers.
Most modern CMS have optimized 404 pages by default, if not, you can easily make your 404 page SEO friendlier by using a plugin or editing your theme templates.

What is an optimized 404 page?
An optimized 404 page should:
- Have the same structure and navigation menus as your website
- Tell visitors in a friendly language that the page they are looking for is no longer available
- Give them alternatives (suggest other related pages)
- Make it easy to go back to the previous page, your homepage, or other important pages
How to check your 404 pages?
Testing how your 404 page looks is very easy, just open a new browser window and type a URL on your website that does not exist. What will be shown in the browser is your 404 page.
Don’t spend too much time optimizing your 404 pages. Just make sure that when a page is not found, it returns a custom 404 page.
8. XML Sitemap Optimization
One of the most important elements of technical SEO is XML sitemap optimization.
An XML Sitemap is an XML file listing all pages/posts on your website that you want the search engines to know about. Besides their title, it also includes the last updated date.
Search engines can use the XML sitemap as a guide when crawling a website. Here is an example of what an XML sitemap looks like:
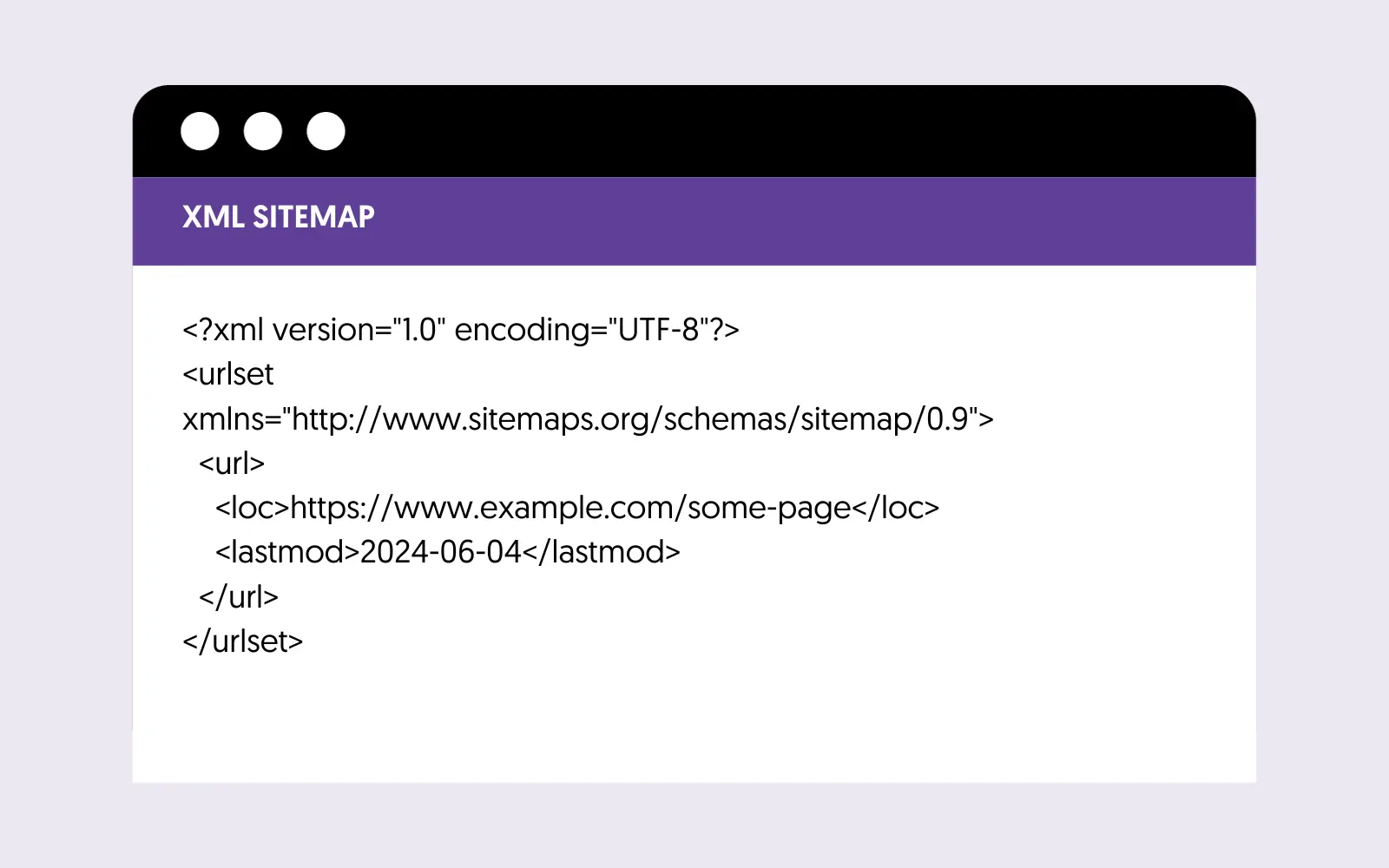
Don’t worry if this looks too technical. The majority of website CMS have the sitemap functionality built-in and all you have to do is select which pages you want to include in your sitemap.
How to Optimize Your XML Sitemap?
XML sitemap optimization is simple, only include in your sitemap the pages that are important for your website. In most cases, these are your pages, posts, and categories.
Don’t include in your sitemap tag pages or other pages that have no original content on their own.
Make sure that your sitemap is automatically updated when a new page is published or when a page is updated.
Use the instructions here to submit your sitemap to Google and check the status.
9. SSL and HTTPS
As part of your technical SEO, you need to make sure that your website has an SSL installed and that it uses HTTPS. HTTPS is a known ranking signal and an additional way to establish trust with your users.
When you install an SSL on your server, your website can be accessed using HTTPS and not HTTP. This indicates that any information transferred between your website and server (such as usernames, passwords, personal data, etc) is encrypted.
In the past, SSL was important for eCommerce websites but nowadays all websites should have an SSL installed.
If you don’t have SSL installed the first thing to do is to contact your hosting provider and ask them to enable SSL on your account then you need to follow a migration procedure to activate SSL on your website without losing your rankings. Adding an SSL is similar to migrating to a new domain so you will have to do it correctly.
10. Website Speed
Another known ranking signal is website speed. Google is mentioning the importance of speed in all their SEO recommendations and studies confirm that faster websites perform better than slower websites.

Tackling website speed is a technical issue and it requires making changes to your website and infrastructure to get good results.
Your starting point is to check your speed using Google page speed insights.
You’ll get recommendations on what you need to change to improve your speed, but as I mentioned above, it’s a technical issue, and you may have to hire a developer to help you.

In general, what you can do to make your website load faster is the following:
- Upgrade your server to use 64 bits operating system
- Upgrade to the latest software versions for your CMS
- Compress your images.
- Minimize the use of plugins
- Optimize and minify your CSS and JS Files
- Using a caching mechanism to serve cached pages to users
- Avoid adding too many scripts in the of your website
- Use asynchronous javascript loading
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
For more information on speed up your website, read: How to increase page speed (easy guide).
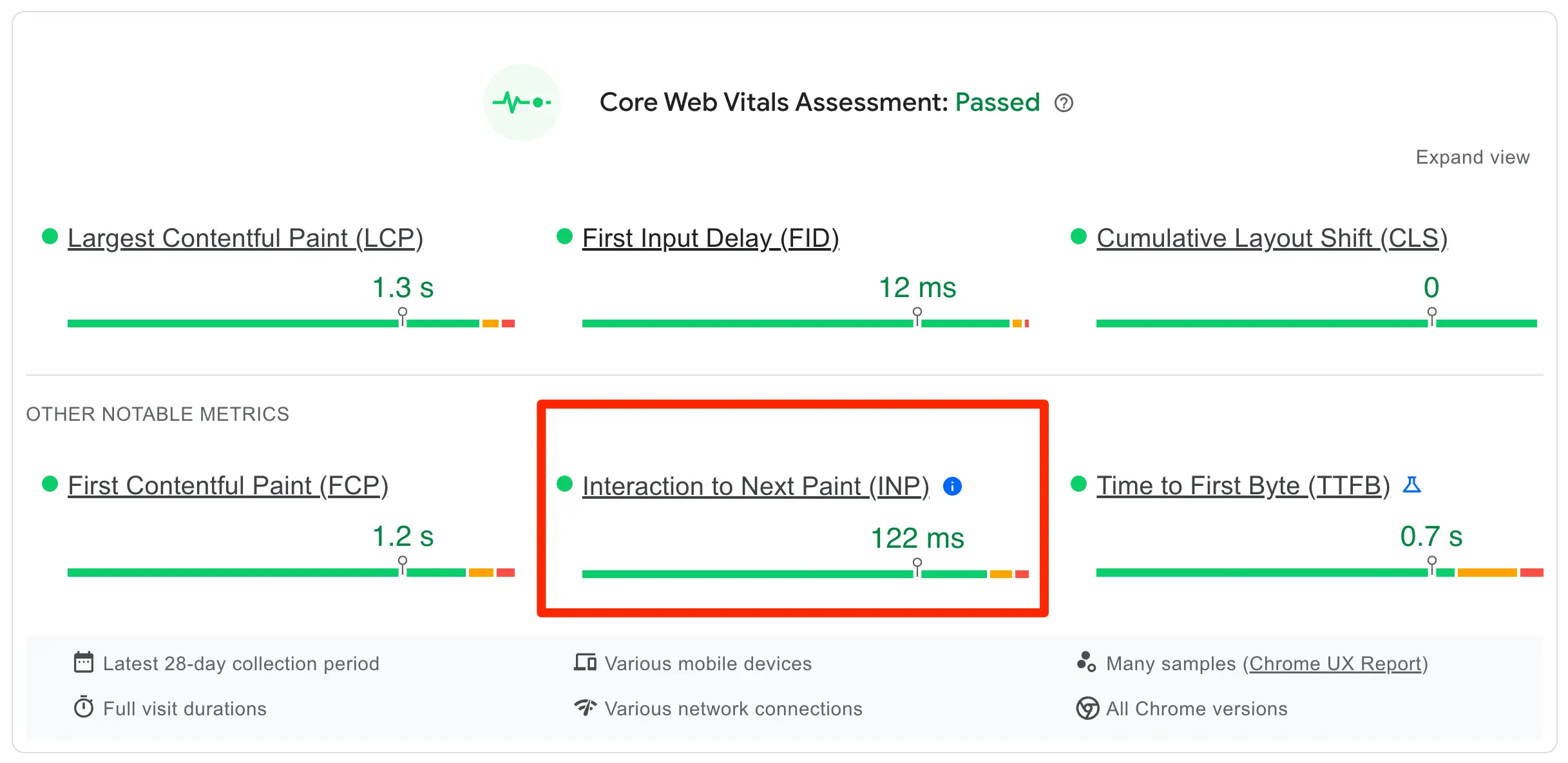
11. Optimize For Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals is a set of metrics used by Google to evaluate the speed of a website. They are part of the page experience ranking system.
To provide a good user experience, sites should strive to achieve these core web vitals values:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) –2.5 sec or less
- First Input Delay (FID) – 100 ms or less
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – 0.1 or less
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – 200 ms or less
Update: INP will replace FID as a core web vitals metric as of March 2024.
To check your website’s core web vitals score, use the core web vitals report in Google Search Console. To get recommendations on how to improve your score, use the PageSpeed Insights report (example shown below).
Again, this is another technical SEO task that can be handled with the help of a developer.
12. Mobile-Friendly Website
Having a mobile-friendly website is not optional but mandatory for two reasons:
- The majority of your users are on mobile
- With the introduction of the mobile-first index by Google, if you don’t have a fast, mobile-friendly website, your rankings will suffer.
Mobile-friendliness is part of technical SEO because once you have a mobile-friendly theme that is properly configured, you don’t have to deal with this again. It’s also a task that requires technical knowledge on how to set it up.
The first thing to do is check your website’s mobile-friendliness using Lighthouse, a Google tool available in the Google Chrome Browser.
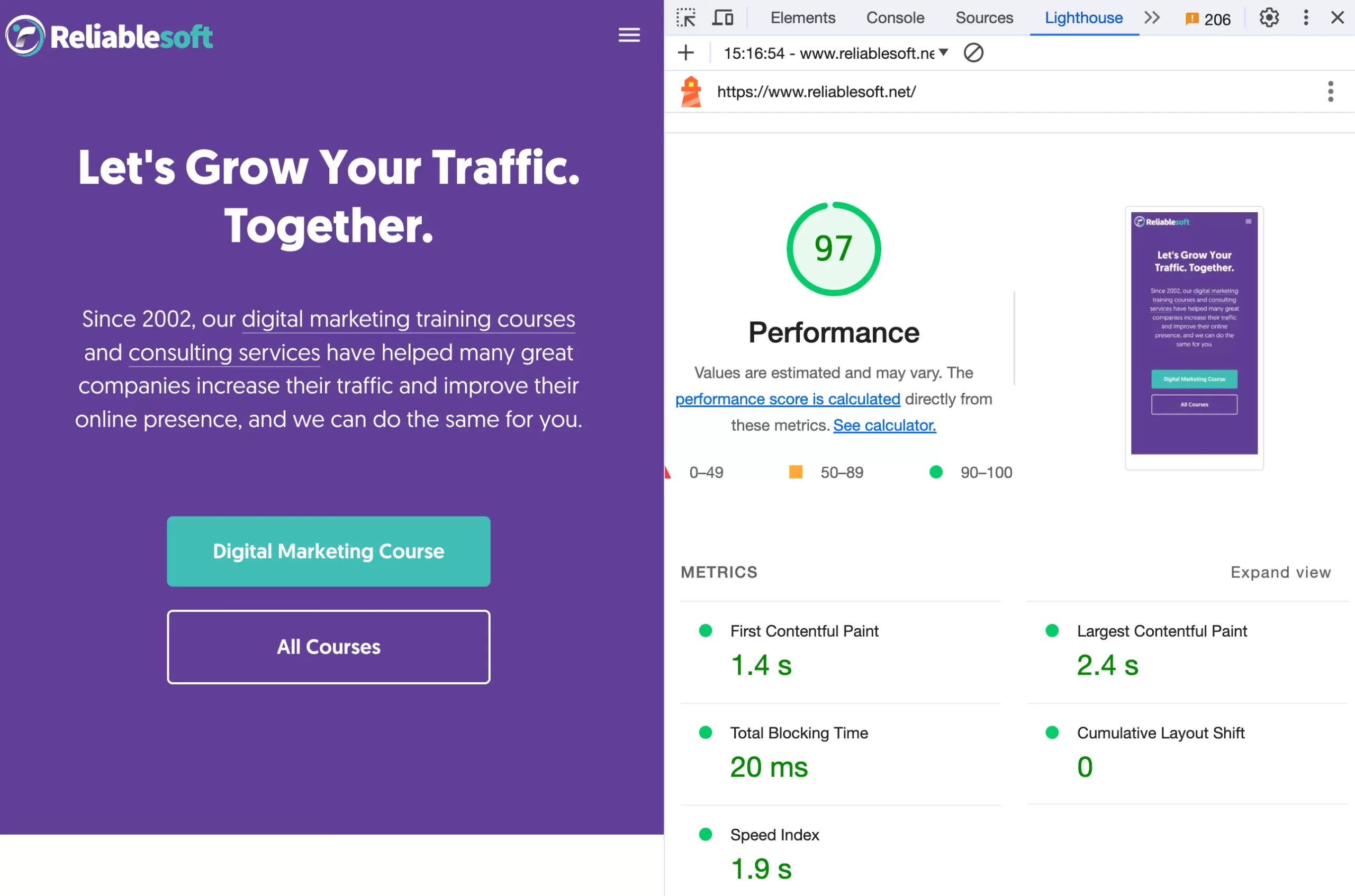
Analyze the results and implement the recommendations until you reach the desired levels.
Besides taking care of these, there are several things you need to know about mobile SEO.
- Your mobile website should have the same content as your desktop site. With the introduction of the mobile-first index, Google ranks websites based on their mobile content, so any content you have on the desktop should also be available on mobile (including any internal links or other elements available on your desktop website).
- Your mobile website should load in less than 3 seconds.
- It is normal to have a lower conversion rate on mobile (compared to desktop), but that does not mean you shouldn’t try optimizing your mobile website as much as possible.
- Avoid using popups or intrusive interstitials on mobile.
If you already have a responsive website, then most probably you won’t have to worry about the mobile-first index, but if you have a separate mobile website on a subdomain or folder, then make sure that it has the same content as your desktop website.
13. Multilingual Websites
If you have content on your website in more than one language, then you need to use the hreflang attribute to give Google more information about your site structure and content.

This will help them serve the right content to users (i.e., to show Swedish people content in Swedish) and help you optimize your SEO by avoiding duplicate content and indexing issues.
It’s a highly technical SEO task that can be configured with the help of a web developer.
For more information on how to handle multilingual websites, read this guide.
Technical SEO Tools
To carry out the most important technical SEO tasks, you need the help of tools.
- Google Search Console – The most complete set of tools is the Google Search Console, provided by Google. With the Google search console, you can test your robots.txt file, submit a sitemap to Google, and find and fix crawl errors.
- Screaming Frog – use it to find broken links, review robots directives, discover issues with canonical URLs, and much more.
- PageSpeed Insights – use it to evaluate your page speed and core web vitals metrics.
- Ahrefs and Semrush – use these tools to perform a technical SEO audit of your website and get recommendations on fixing errors.
Technical SEO Video
Watch the video tutorial to learn what technical SEO is and how it works.
Learn More About Technical SEO
To continue learning about Technical SEO, read the following guides:
- Best Technical SEO Courses – A list of the best technical SEO courses to take online and learn technical SEO fast.
- SEO Starter Guide – a guide on SEO (including Technical SEO) by Google.
- SEO Audit Checklist – To further check the optimization level of your website, you can perform a general SEO Audit, which includes many more checks that go beyond technical SEO.
- Learn SEO – a step-by-step guide to learn SEO.
Conclusion
Technical SEO consists of a number of checks and settings you need to optimize to help search engines crawl and index your website without any problems.
In the majority of cases, once you get your technical SEO right, you won’t have to deal with it again, other than doing periodical SEO Audits.
The word technical implies that you need to have some technical knowledge to carry out some of the tasks (like page speed optimization, adding structured data, etc.) but it’s necessary to do it otherwise your website won’t reach its full potential.





