Google processes an average of 3 billion searches a day. To be able to provide relevant responses to all these queries, Google must continually find new websites to add to its search engine.
In this guide, you’ll learn how Google finds websites for its search engine and what it sees when looking over your site.
Why is it important to know how Google crawls a website?
SEO is not static. It is a constantly evolving process as Google regularly makes updates to how it looks to provide searchers with the best possible results.
If you want to get your pages to the top of the rankings and have them stay there, you need to know how search engines work.
It begins with crawling, the process Google uses to find new pages around the web.
When you know how Google crawls websites, you can ensure your pages are always visible to Google and ready to be used in search results.
Knowing the way Google crawls websites will also help you optimize your pages for the search terms you want to rank for.
How does Google find a website?
Because there isn’t a single centralized database of everything on the internet, Google must continually work to find relevant pages to show in its search results.
The search engine has three primary functions for finding and listing content; crawling, indexing, ranking.
1. Crawling
Search engines like Google find websites through a process called crawling. The process begins when Google sends out software bots known as crawlers or spiders across the internet to find new content.
The search crawlers start with web pages used in previous crawls. When a crawler visits a page it will look for links to other pages to add to a list of pages to crawl.
To know what a page is about, Google will render the page and analyze the content and overall layout. Google uses mobile-first indexing which means that will look at the mobile version of a website first when analyzing its pages.
2. Indexing
Google stores the websites it finds while crawling in their index.
A web index serves as a database for information available on the internet. When a page is in Google’s index, it has the chance to appear as a result to search queries.
3. Ranking
Ranking is the process of determining which pages will appear in the results for different search queries.
When someone conducts a search in Google, the search engine runs an algorithm to see which pages in the index are most relevant to that particular search query.
It then serves these pages to the searcher in the results page, starting with the most relevant page.
Video: How Search Engines Work
Crawl Budget
Crawl budget is the number of your web pages Google will crawl during a period of time.
As Google doesn’t have unlimited resources, it is unable to constantly crawl every single page for every website. The crawl budget determines how many URLs on a particular website Google will crawl.
Crawl budget will not be an issue for most websites. Unless you have a massive website like an eCommerce store with thousands of pages, the crawl budget for your site will likely be more than enough to cover all the pages you want to have indexed.
That being said, it is still important to understand how your crawl budget is determined.
There are two factors that are used to decide the crawl budget:
- Crawl rate limit: The amount of crawling a website can handle without experiencing performance issues.
- Crawl demand: The degree to which it is worth Google crawling a URL based on popularity and how often it is updated.
Crawl limit helps ensure that search crawlers do not overload your web server with too many requests. Search engines will take into account how often requested URLs timeout or return server errors.
They will also look to see if your website uses a shared hosting platform as this will limit the available server resources.
How to get Google to crawl your website
It is possible for Google to find and crawl your website without any action on your part. However, you can never be certain Google will find your site on its own, so it is recommended to take steps to ensure your website is crawled and indexed.
There are various methods you can use to help Google’s crawlers find your website. The most effective are:
Create an XML sitemap
A sitemap is a document that lists the URLs of your web pages. This helps make it easier for the crawler to find your pages as it no longer depends only on the internal links from your pages and external links from pages around the web.
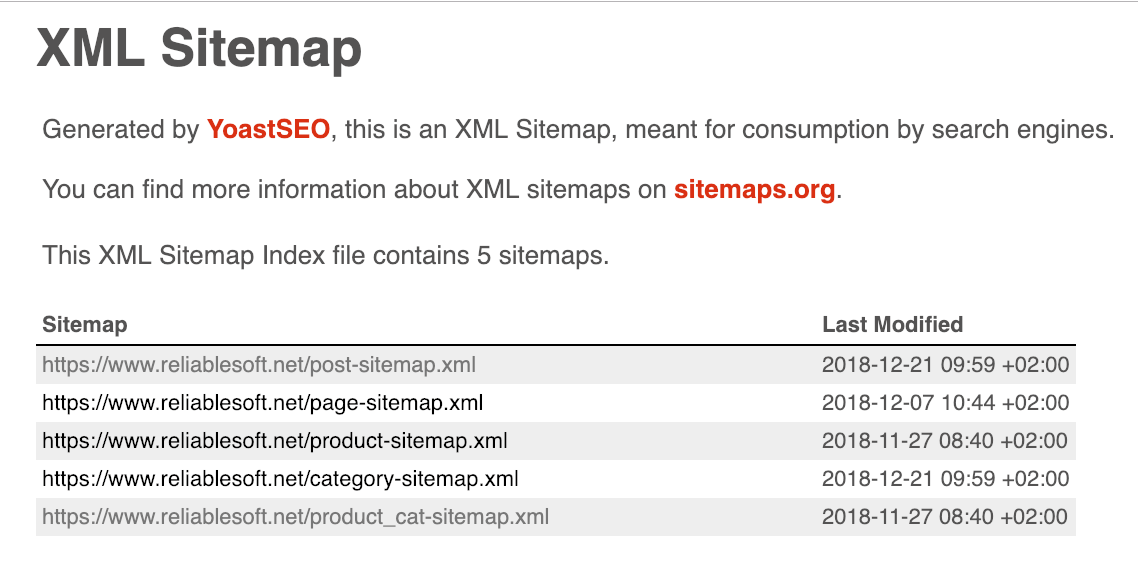
There are a variety of ways you can create an XML sitemap.
You can choose to manually create an XML file with your URLs or you can use one of several available tools to handle the process for you.
One popular option is Screaming Frog, a desktop software that can generate a sitemap for websites with up to 500 pages.
Another viable solution for WordPress users is the Yoast SEO plugin which will automatically generate a sitemap.
Create a Google search console account and submit your sitemap
Google Search Console is a platform that allows you to track how your website performs in the Google search index.
You can see which of your pages are in Google’s search index and where different pages are ranking in search results.
This includes a list of all the keywords each page has ranked for, along with important stats such as:
- Total clicks
- Total impressions
- Click-through rate
- Average position
With Search Console, you can upload your sitemap directly to the platform.
This is the fastest way to have Google index your site as after submitting your sitemap, Google will crawl the document to find all the pages you want to include in the index.
Search Console has other useful tools to help ensure your pages are indexed properly.
One of these is the URL inspection tool which you can use to test URLs to see if Google can find them and if they are eligible to be indexed.
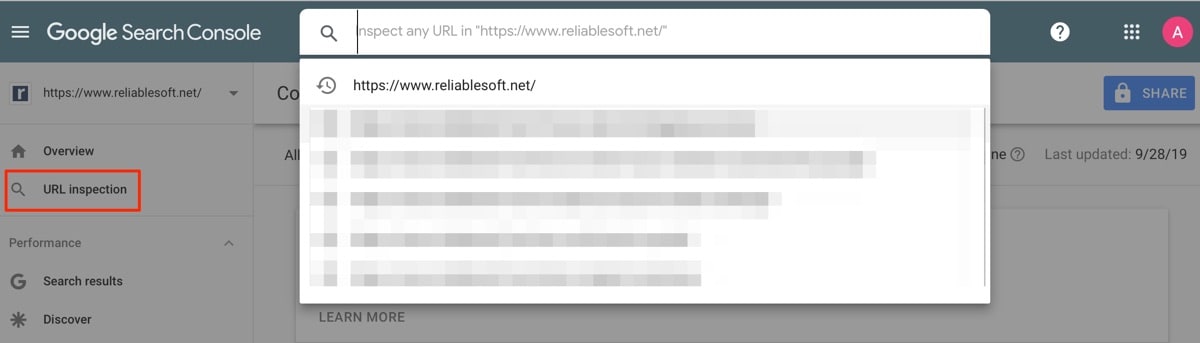
It will also check the page for errors and mobile usability.
If a page is eligible for indexing, you can submit a request right on the URL inspection page and Google will crawl and add the page to the index.
If Google has any issues when crawling your pages, you will receive error messages on your dashboard with details of the issue and how to fix it.
How to see if your site is indexed in Google
You can quickly see if your site is indexed by performing a site search in Google.
Go to Google, and enter the following (using your website name) in the search bar:
site:yourwebsite.com
The results will include all your web pages that are indexed by Google.
If the search comes back without any results then your website is not currently in Google’s index.
You can check to see if a specific URL is indexed by adding the URL slug to your domain in the site search.
Another way to check the index status of your web pages is to use the URL inspection tool inside of Google Search Console.
Simply type the URL into the search bar at the top of the page and Google will let you know if the page is currently indexed.
How does Google see your website?
When a crawler arrives on your website it will look for a robots.txt file before continuing to crawl the pages on the site.
The robots.txt file provides instructions for search engines on how to treat the site. In this file, you can tell Google not to crawl or index certain pages.
The robots.txt must be stored in the website’s top-level directory, otherwise, Google will not be able to find it.
After the crawler has read the instructions, it will begin to crawl the site, starting with the home page.
Crawlers need to look at a variety of elements when evaluating your web pages.
Here are the elements of a webpage that are most important for the Google crawler:
Meta Tag directives
Meta directives are snippets of code that provide crawlers instructions on how to handle your web pages. With these tags, you have more control over how your website appears in search engines.
Meta directives are normally executed via Robots Meta Tags in the
of your HTML pages.
Here are the most common meta directives:
- index/noindex: This directive instructs search engines whether the page should be crawled and included in Google’s index. Adding the noindex tag to a page tells Google that you do not want that page to appear in search results so crawlers will skip over the page.
- follow/nofollow: This directive tells Google whether it should follow links on the page. All pages have a follow tag by default which communicates to crawlers to follow the links on your page and pass link juice to those URLs. Adding the nofollow tag tells search engines to not follow the links or pass any link juice to the URLs on the page.
- noarchive: This directive restricts Google from saving a cached copy of the page. Without this tag, Google will use cached versions of the page to always have a visible copy indexed that searchers can access. This directive can be helpful if you run an eCommerce site where your prices change often.
Published date, last update date
To provide the most relevant results to searchers, Google uses the freshness of content as a ranking factor.
The main criteria Google will examine when evaluating the freshness of your content are the publish date and the date of the most recent update.
For many types of search queries, Google will display the publish date next to the listing on the results page.
Page title
A page title is an HTML title tag that appears as the name of the page in search engine results.
Your page titles play an important role in SEO as they help determine if searchers click your listing.
Google uses click-through rates when deciding how relevant your pages are for certain keywords. This means that if your listings get a low level of clicks relative to the number of impressions, your pages will be positioned lower in the results.
Having a relevant and engaging page title will help ensure that your listings receive a solid click-through rate.
Page meta description
Meta descriptions are an HTML element in your meta tags that help describe your web pages.
They appear as a small snippet of text beneath your page title (headline) in search results.
Like page titles, meta descriptions are an important ranking factor as they play a big part in getting searchers to click-through to your website.
Page headings (H1 tag, etc)
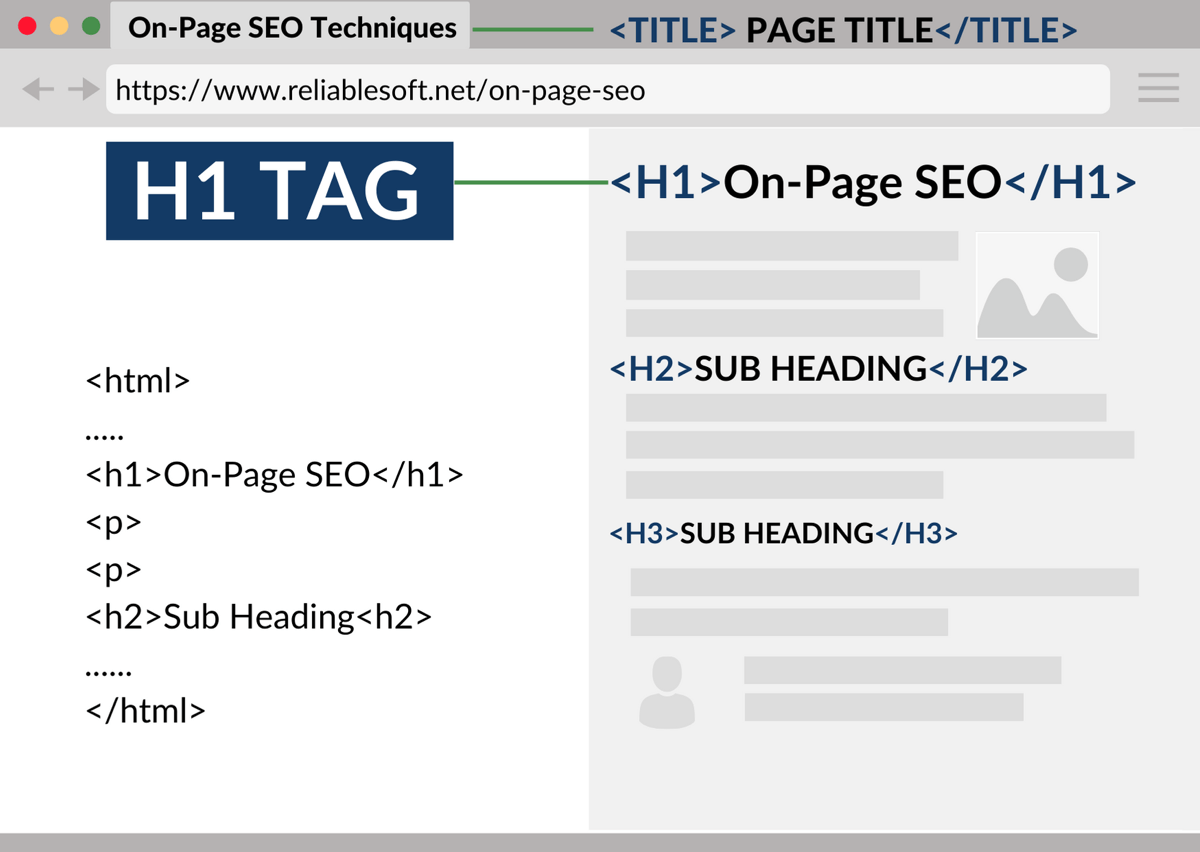
Headings provide structure to your web pages by breaking content up into different sections.
Headings are applied to text through the use of HTML tags.
For example, an h1 tag is used to indicate the primary heading of the page (usually the page title). Each subheading is given a different tag starting with h2 and then moving to h3, h4, etc.
Headings play a role in SEO as they help crawlers understand the context of your content easier. They also help improve the usability of pages by making content easier to navigate.
The h1 tag is the most important tag as it tends to contain the primary target keyword and describes exactly what the page is about. Each page should only have one h1 heading.
You can use as many subheading tags (h2, h3, h4) as needed. Look to include the target keyword frequently but without overdoing it.
Content
Content is the foundation of any web page and is where you will provide searchers with the answers to their questions.
Without quality content, it will be difficult to rank for competitive keywords.
Here are some of the factors Google will evaluate when crawling your content:
- Keyword density: How often you use a keyword on a page. Google will use this to determine the topic of the page.
- Degree and frequency of updates: Updating your content can improve the freshness of pages.
- Table of contents: This makes it easy for Google to understand a page’s content and improves usability.
- References and sources: Citing reputable sources can be a sign of quality to Google.
Crawlers will look to see if any of your content is replicated across pages. You want to avoid having any duplicate content as it will negatively affect your search engine rankings.
The length of your content also plays a role in how well pages rank as longer pages tend to perform better.
As a general rule, it is recommended to have at least 300 words per page.
If you have a page where reaching this amount of words is unrealistic, you can noindex the page to avoid being penalized for thin content.
Internal and external links
Using internal links on your web pages will improve the crawl depth of your website and will help search engines find and index more of your pages.
External links also impact how Google sees your website. Having links to authoritative and relevant content sends trust signals to Google and adds context to your pages, helping crawlers understand them better.
It also improves the quality of your content by connecting readers with other useful material.
Alt text for images

Image alt text is an HTML attribute given to images that provides a text alternative for search engines.
It is an important SEO factor as search engines and crawlers are not able to understand an image based on its visual appearance.
With alt text, search engines have readable text they can use to discern the context of the image.
Adding alt text with target keywords to images can send relevancy signals to search engines, helping them to rank your content higher.
Video schema
Like images, search engines require extra assistance to truly understand your video content.
Instead of adding alt text, you need to add schema markup to your videos.
Schemas are HTML tags that help search engines understand your videos better by providing more information about the video’s content.
Here are the schema tags you should add to all your videos:
- Name: A required tag that includes the title of the video. It is recommended to use a target keyword in the title when appropriate.
- Description: Another required tag that provides a description of the video. Look to keep the description concise and engaging as it will appear in a rich snippet in search results.
- Duration: This tag notes the length of the video. Providing this information is important as video length plays a big role in which content searchers choose to watch.
- ThumbnailURL: This tag points to the URL for the file of the thumbnail you want to use for the video. This is an important tag as a quality thumbnail image can lead to better engagement from searchers.
- ContentURL: This tag contains the URL that points to the video URL file. It is important to make this accessible to Google as it will help generate a video preview.
Keyword usage
When deciding how to rank pages for different search terms, search engines will look for the associated keywords throughout the content.
It is a common belief among seasoned SEO experts that Google weighs the first couple hundred words of your content more heavily when evaluating your pages.
Using target keywords towards the beginning of content can help search engines quickly understand what a page is about, allowing the pages to rank higher for search terms.
BERT and natural language processing
BERT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, is a natural language processing (NLP) framework produced by Google to help the search engine better understand the context of words in search queries.
In the past, computers had difficulty processing language as there are many words that are ambiguous or have multiple meanings.
This made it a challenge for search engines to understand the intent behind a search and provide the appropriate results.
BERT helps Google understand searches better by outlining the relationships between words and analyzing their contextual meanings.
This leads to better results for conversational search queries as the ranking pages are a better match for searcher intent.
The best way to optimize your pages for BERT is to include enough related keywords in your content.
This will ensure that your content is contextually rich and will send signals to Google that your page matches searcher intent.
JavaScript
Many websites use some form of JavaScript to add interactivity to their pages. While this can help improve user experience, it can create some SEO challenges.
JavaScript can make it difficult for Google to read your pages, leading to errors. It also takes longer for Google to crawl and index as there are more steps involved than when crawling HTML.
With JavaScript, Google needs to download, parse, and execute the code to be able to render the page.
You can help improve Google’s ability to crawl your JavaScript pages by adding instructions to your robots.txt file that ensures Googlebot is able to access and download the resources needed to render the page.
Mobile usability (errors are reported in Mobile Usability Report in GSC)
Google includes mobile usability as a ranking factor when evaluating pages. This means that your mobile pages must provide users a high-quality experience if you want your pages to rank high for relevant keywords.
Google provides a tool you can use to test the mobile-friendliness of your site.
Google will pick up on any mobile usability errors when crawling and will report them in Google Search Console.
To view any errors simply click on the mobile usability tab. From there you will see a list of the mobile pages experiencing errors along with more details about the specific issue.
After seeing the cause of an error you can fix the issue on your website and then notify Google that you corrected it. They will then rescan the page and remove the error message.
Key Learnings
Google finds new websites by sending its crawlers known as Googlebots around the web. The crawlers move to and from the links on different pages to navigate the internet.
As they go, crawlers save the pages they find in an index that is used to serve the most relevant pages when someone searches for something in Google.
The most effective way to get Google to crawl your website is to generate a sitemap (a document listing all your site’s URLs) and upload it to Google Search Console.
Google will then crawl the sitemap and index all the pages you have listed.
You can have Google skip over pages that you don’t want to be indexed by adding instructions to your robots.txt file or applying a noindex tag to the page.
Google’s crawlers will analyze a myriad of elements from your website when determining where to position your pages in search rankings.
This includes the content itself as well as the metadata, keyword usage, publish date, mobile usability, and more.
When you know what Google looks for when it crawls websites, you are able to optimize your pages to improve your search engine rankings.





